Strikelink Commodore Wifi Modem (ESP8266 ESP-12E)

- Hardware Build
- Software
- Official Instructions
OVERVIEW
(Full disclosure: some content from https://1200baud.wordpress.com/2017/03/04/build-your-own-9600-baud-c64-wifi-modem-for-20/)
I wanted to get my C64 talking to the web, or at least some of those migrated telnet-based BBSes from back in the day, at first! I looked through the various options, and there are two that stood out to me for various points.
- Ultimate-II+L
- I consider this the Grand Poobah of C64 modern conveniences. Tape/disk/cartridge hosting and emulation, ethernet connectivity, ROM-swapping, I mean this sucker is a pretty awesome plug-n-play device if you just wanna get rocking now. Also if you have a spare $150 laying around (for U.S. readers, original price is around 122 Euros)
- Strikelink Wifi
- For DIY cheap-asses like myself, this is the way. Solder a NodeMCU dev board to a custom PCB, along with a C64 userport plug (from Amazon, natch), write the firmware to the board, slap it on the Commie and get to dialin!
Okay, there are a few more steps involved in getting the second option to work, but that’s the price we DIY frugal types have to pay. If you value your time more, you’ll have to pay somebody else to invest theirs instead, e.g. Buy The Premium Option.
For you folks with some extra cash laying around and looking for a purpose in life, you can get these things here:
- https://retrorewind.ca/c64-wifi-modem
- https://www.cbmstuff.com/index.php?route=product/product&product_id=58
- https://www.retro-updates.com/product/9643396/commodore-c64-128-wifi-modem
For the rest of us control freaks, we can do our own thing and have full control over the final results. Here’s how to make your own C64 Strike Link wifi modem! (Don’t worry about how long this looks. Just read through it carefully and as you start your project, you’ll see it’s really not that difficult, I’m just taking the time to include all the little details that matter so you can succeed without all the little gotchas I experienced, the first time)
You will need to start by procuring the necessary tools, and have some basic knowledge of a few things. These are the bare minimums- more skilled makers will expand on it as they get ideas over time
Tools
- Soldering iron (at bare minimum)
Knowledge
- How to solder (SAFELY, DUH!)
- How to work with Arduino and similar microcontrollers for simple programming
Now you need some materials and software. If you don’t already have the hardware components, you can order them below, but the wait times are generally pretty acceptable (unless it’s near the Christmas holiday!)
- Hardware
- ESP8266 12-E microcontroller (about $17 for 3 at time of writing)
- Base circuit board (manufactured by PCBWay or Elecrow) using these Gerber files
- Commodore user port edge connector
- These can be hit-and-miss to find, Amazon or Ali Express are the most reliable soruces.
- Software
- Arduino IDE or VS Code
- CP210x USB to UART Bridge VCP Drivers
- StrikeLink source code (also available in Software tab above)
- Commodore Color Graphics Manipulation System terminal (we don’t know either, just call it CCGMS and everybody else will smile and nod warmly)
ASSEMBLY

Fire up your soldering iron. While it’s heating up, lay out your work space.
Identify the PCB top side. If you had boards made from the linked Gerber files, it will be the side with the words “Strikelink Wifi” on it, near the bottom left corner

The ESP8266 controller board will mount to the PCB, with the microUSB connector facing away from the edge pads (so in the picture above, spin the controller 180 degrees). This part is a bit of a faff, as the British like to say. The pins won’t always line up just so to let you simply plug it into the board. You’re likely going to have to work carefully to get first one row of pins to line up and slide into the holes, then the other.

BE GENTLE, don’t just shove a screwdriver into a pin to try to jam it in; that’s how you get bent and broken pins. Instead just nudge them around and keep trying patiently to get things in line. Eventually it will just happen, and the board will slide down snugly and fully.

Flip the board over and solder the pins down carefully. Touch the iron to the pin to start transferring some heat to it, then touch the solder to the point where the iron and pin meet. The solder should melt and run down the pin to pool up near the base nicely. You’ll get the gist of it after a couple of pins, and you see how solder behaves.
If you already know how to solder, ignore me and do your thing.

Now it’s time to get the connector soldered on. Take a close look at that connector. You will notice there are two rows of pins on the back side. The modem board will actually fit in between those rows of pins, with each pin lining up with a pad on the board.

Slot the board in between those rows of pins, make sure each pin aligns with a pad on the board, then start soldering them down. Make sure to apply some flux to these pins before starting, that will help the solder flow more evenly in place and form a nice solid bond.
Take your time, make sure they’re nice and neat, and don’t forget to do the other side of the board too!

It’s done. Holy shit, you did it!
So basically this board just lets us make a few connections to the relevant GPIO pins on the controller to the C64’s user port, so the computer can connect with it just like it would have an OEM modem. After we get the firmware installed and configured on this little devil, the Commodore won’t know the difference; it’ll simply be working with the fastest dial-up connection it has ever seen! 🙂
PROGRAMMING
You’ll want a spare computer for this part. It could be anything that can run the Arduino IDE or VS Code. There are other ways to do this, but this is the method I learned, so as to circumvent an unexpected firmware issue. More on this later.

Download and install Arduino IDE or VS Code.
Pretty straightforward, really, depending on your preferred OS.
If you’re preferring to use VSCode, run over here to get the board connected properly first, then come back here for the actual modem firmware config/install. If you’re in Arduino IDE (hopefully v2.0+), read on!

Once installed, go to File > Preferences, and enter this URL into the “Additional Boards Manager URLs” field:
http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json

Open the Boards Manager. You can go to Tools > Board > Boards Manager… or you can simply click the Boards Manager icon in the left-side corner.
Search for ESP8266 and press the install button for esp8266 by ESP8266 Community.

In the main IDE window, select the dropdown near the top that says “Unknown board”, and Select Other Board and Port. Search for your actual board model and select it. In my case, (and yours, if you used my link to it above), the board is NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)
You should see a selectable COM port as well. If you do NOT see a COM port available, you might need drivers for your computer to recognize the board. For that, run over here, download and install the drivers appropriate for your OS, then try again.
Now here is where we do just a little tinkering to modify the (already-modified) firmware, depending on your needs. Rather than ask you to download some random file and open it on your computer, I’m going to post the entirety of the source code over here for your review. You can copy and paste it to your Arduino IDE once you’re satisfied it’s not going to boot up and take over the world.
I have modified the code in only a few places:

These additions have helped reduce weird long lags for wifi connections I’ve experienced with these boards, from time to time

If your wifi name has an underscore (“_”), you won’t be able to set the network name from the C64 as was originally intended, because Commodore had no underscore in its character set. However you can sneak one in by hard-coding it here.
If you need to hard-code yours, swap where the “//” are between the ssid and pass variable lines

The numbers “60” and “61” used to be “20” and “21”. They define how many seconds the device will wait until it decides it can’t connect to the wifi network. For some boards, this isn’t enough, and they can take longer to get a connection established (hence the code additions referenced above, as well)
Otherwise, the code has been left alone to do its magic. Once you’ve pasted the code into your IDE and are satisfied it’s ready to run for you, send it to the board.

In Arduino IDE, this is done right the right-arrow button, just to the right of the checkmark button, at top-left of the IDE window

You should be seeing things happening in the console portion of the IDE near the bottom of the window. If you don’t see any activity, the board might not be ready to communicate.
Push the Flash button to the left of the microUSB plug until you see the status light change, and then, if flashing hasn’t started on its own, trigger it again from the Arduino IDE.

The program compiles, then uploads to the board. You will see a progress report as it reaches completion.
When it’s done and ready, you’ll see the lines:
"Leaving...
Hard resetting via RTS pin..."as the last entries in the console window. That’s it! Programming over, unplug that bad boy and let’s test it out!
CONNECTING
You will need a copy of the popular CCGMS terminal program. This has been modded by Alwyz, the same awesome person brought the StrikeLink hardware and software into working, singing harmony! You can get CCGMS2021 here, or if you run into issues, some have reported an easier time with CCGMS2017 instead.
Now, the choice of downloading .d64 or .crt version of the program I leave to you. Discussing the differences between the formats and how to use them is outside the scope of this article that is getting big in the britches as it is. Suffice it to say .d64 is a floppy disk image, .crt is a cartridge ROM version. Getting those loading on your Commodore should be second nature to you now, right? You know, since you’re already walking the path of making a modem for this machine, right??
Okay fine, if you don’t have a 1541/1541-II/1571 floppy drive, you can fake it with various devices. SD2IEC is a common means of reading SD cards via the drive’s serial (IEC) port. For compatibility, my personal favorite is Pi1541, which emulates a 1541 drive perfectly.
Let’s assume you know what you’re doing at that end of the spectrum already, and move along getting this StrikeLink chattering with the world!

With your C64 powered OFF, Plug the Strikelink WiFi into the C64 User Port, WiFi Logo side UP.
WARNING: NEVER plug in or remove devices while the computer is turned on, and NEVER plug that ESP8266 into a USB cable unless it is UNPLUGGED from the Commodore!

Turn on the computer, and load CCGMS using tapecard/pi1541/sd2iec/jank-ass 1541 floppy drive (actually if you have a 1541 and working floppies, you are an idol with infinite patience and deserve tribute from all who cross your path!)

Press F7 to enter the program settings menu, select UP9600 / EZ232 under modem type, and change the baud rate to 9600 baud
Press Return to return to Terminal Mode

Press Return. Your Strikelink should say hello to you!
First, please pardon the b&w image. I (was) in the middle of a VIC-II-dizer upgrade. Second, you may notice mine went right to connecting to the wifi after “saying hello”. That’s because I hard-coded my wifi info as described previously!
If you did NOT hard-code your wifi network details, press F8 to enter Anscii Mode. Do not skip this step. You need the terminal to be in a “pure” text mode, so what you type is what is saved. That is not the case with Graphics Terminal mode.
Type and press return: at$ssid=[YourSSID]
Type and press return: at$pass=[YourPassword]
Type atc1 to connect, and you should see it connecting to your wifi access point
Once the connection is established, you can type at&w to write your settings to the Strikelink’s memory.
You are now online and ready to start connecting to some good old-fashioned (and some new!) BBSes
Check here for some interesting ones to get you started!
FUTURE PLANS
Seems like everybody has a case for these things, but I’m not the type to leave well enough alone, so…
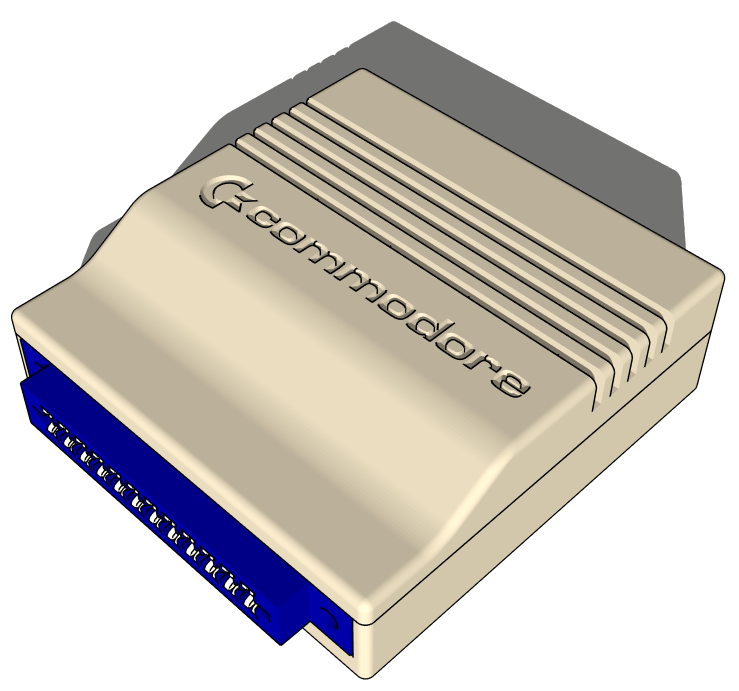
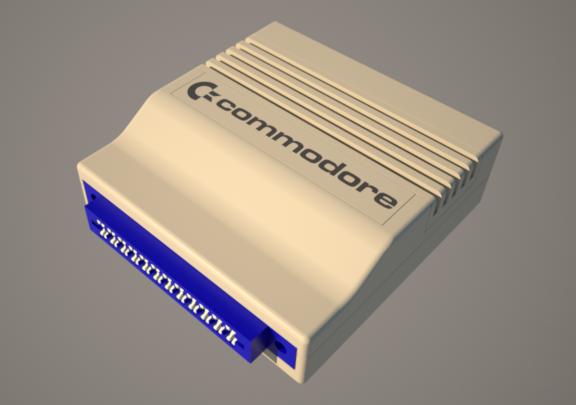

I’ve got the 3D model all set, now just doing a bunch of testing with the 3D printer to see what’s what. Updates to come as they’re available!
By the way, those “at” commands are custom extensions to the old Hayes modem commands. You might remember “atdt” to dial out on touch tone lines, or “ath” to hang up, or the fave of ragequitters everywhere, “+++”, which basically interrupted any-dang-thing that modem was doing and brought it to attention poste-haste so you could “ath” the heck out of there before anybody realized it was you hacking the Gibson all along! Here is the full command list that StrikeLink is ready to acknowledge:
COMMANDS
| DIAL HOST | ATDTHOST:PORT |
| SPEED DIAL | ATDSN (N=0-9) |
| SET SPEED DIAL | AT&ZN=HOST:PORT (N=0-9) |
| HANDLE TELNET | ATNETN (N=0,1) |
| PET MCTERM TR | ATPETN (N=0,1) |
| NETWORK INFO | ATI |
| HTTP GET | ATGET |
| //SERVER PORT | AT$SP=N (N=1-65535) |
| AUTO ANSWER | ATS0=N (N=0,1) |
| SET BUSY MSG | AT$BM=YOUR BUSY MESSAGE |
| LOAD NVRAM | ATZ |
| SAVE TO NVRAM | AT&W |
| SHOW SETTINGS | AT&V |
| FACT. DEFAULTS | AT&F |
| PIN POLARITY | AT&PN (N=0/INV,1/NORM) |
| ECHO OFF/ON | ATE0 / ATE1 |
| VERBOSE OFF/ON | ATV0 / ATV1 |
| SET SSID | AT$SSID=WIFISSID |
| SET PASSWORD | AT$PASS=WIFIPASSWORD |
| SET BAUD RATE | AT$SB=N (3,12,24,48,96,192,384,576,1152)*100 |
| FLOW CONTROL | AT&KN (N=0/N,1/HW,2/SW) |
| WIFI OFF/ON | ATC0 / ATC1 |
| HANGUP | ATH |
| ENTER CMD MODE | +++ |
| EXIT CMD MODE | ATO |
| QUERY MOST COMMANDS FOLLOWED BY ‘?’ |
TROUBLESHOOTING
If you’re having a problem with anything happening when you dial out to a site, or maybe happening very wrongly, you might have the wrong comm rate set. Your StrikeLink is capable of multiple speeds, but if you’re not sure what it’s currently set to, press and hold the reset (RST) button on the controller (next to the USB plug) for 5 seconds. The StrikeLink will fall back to 300baud (bits/second). If you hit f7 and set CCGMS to use 300 baud as well, you should be able to resume communication on-screen from there.
AT$SB=96 will set the StrikeLink back to 9600 baud, make sure you go back into f7 menu, set baud rate to 9600 in CCGMS, and you can then re-try connecting elsewhere. Don’t forget your terminal modes! Graphics mode is for other Commodore-hosted boards or those indicating they are “PETSCII-compatible”. Otherwise, you can switch to ANSCII (color ANSI) mode if what you’re receiving doesn’t look right.
/*
Modified by Deadweasel <deadweasel@gmail.com> to address common network connectivity quirks on some variants of ESP8266
WiFi SIXFOUR - A virtual WiFi modem based on the ESP 8266 chipset
Copyright (C) 2016 Paul Rickards <rickards@gmail.com>
Added EEPROM read/write, status/help pages, busy answering of incoming calls
uses the readily available Sparkfun ESP8266 WiFi Shield which has 5v level
shifters and 3.3v voltage regulation present-- easily connect to a C64
https://www.sparkfun.com/products/13287
based on
ESP8266 based virtual modem
Copyright (C) 2016 Jussi Salin <salinjus@gmail.com>
https://github.com/jsalin/esp8266_modem
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <ESP8266WebServer.h>
#include <EEPROM.h>
#include <ESP8266mDNS.h>
// These translation tables are not used yet.
static unsigned char petToAscTable[256] = {
0x00,0x01,0x02,0x03,0x04,0x05,0x06,0x07,0x14,0x09,0x0d,0x11,0x93,0x0a,0x0e,0x0f,
0x10,0x0b,0x12,0x13,0x08,0x15,0x16,0x17,0x18,0x19,0x1a,0x1b,0x1c,0x1d,0x1e,0x1f,
0x20,0x21,0x22,0x23,0x24,0x25,0x26,0x27,0x28,0x29,0x2a,0x2b,0x2c,0x2d,0x2e,0x2f,
0x30,0x31,0x32,0x33,0x34,0x35,0x36,0x37,0x38,0x39,0x3a,0x3b,0x3c,0x3d,0x3e,0x3f,
0x40,0x61,0x62,0x63,0x64,0x65,0x66,0x67,0x68,0x69,0x6a,0x6b,0x6c,0x6d,0x6e,0x6f,
0x70,0x71,0x72,0x73,0x74,0x75,0x76,0x77,0x78,0x79,0x7a,0x5b,0x5c,0x5d,0x5e,0x5f,
0xc0,0xc1,0xc2,0xc3,0xc4,0xc5,0xc6,0xc7,0xc8,0xc9,0xca,0xcb,0xcc,0xcd,0xce,0xcf,
0xd0,0xd1,0xd2,0xd3,0xd4,0xd5,0xd6,0xd7,0xd8,0xd9,0xda,0xdb,0xdc,0xdd,0xde,0xdf,
0x80,0x81,0x82,0x83,0x84,0x85,0x86,0x87,0x88,0x89,0x8a,0x8b,0x8c,0x8d,0x8e,0x8f,
0x90,0x91,0x92,0x0c,0x94,0x95,0x96,0x97,0x98,0x99,0x9a,0x9b,0x9c,0x9d,0x9e,0x9f,
0xa0,0xa1,0xa2,0xa3,0xa4,0xa5,0xa6,0xa7,0xa8,0xa9,0xaa,0xab,0xac,0xad,0xae,0xaf,
0xb0,0xb1,0xb2,0xb3,0xb4,0xb5,0xb6,0xb7,0xb8,0xb9,0xba,0xbb,0xbc,0xbd,0xbe,0xbf,
0x60,0x41,0x42,0x43,0x44,0x45,0x46,0x47,0x48,0x49,0x4a,0x4b,0x4c,0x4d,0x4e,0x4f,
0x50,0x51,0x52,0x53,0x54,0x55,0x56,0x57,0x58,0x59,0x5a,0x7b,0x7c,0x7d,0x7e,0x7f,
0xa0,0xa1,0xa2,0xa3,0xa4,0xa5,0xa6,0xa7,0xa8,0xa9,0xaa,0xab,0xac,0xad,0xae,0xaf,
0xb0,0xb1,0xb2,0xb3,0xb4,0xb5,0xb6,0xb7,0xb8,0xb9,0xba,0xbb,0xbc,0xbd,0xbe,0xbf
};
static unsigned char ascToPetTable[256] = {
0x00,0x01,0x02,0x03,0x04,0x05,0x06,0x07,0x14,0x09,0x0d,0x11,0x93,0x0a,0x0e,0x0f,
0x10,0x0b,0x12,0x13,0x08,0x15,0x16,0x17,0x18,0x19,0x1a,0x1b,0x1c,0x1d,0x1e,0x1f,
0x20,0x21,0x22,0x23,0x24,0x25,0x26,0x27,0x28,0x29,0x2a,0x2b,0x2c,0x2d,0x2e,0x2f,
0x30,0x31,0x32,0x33,0x34,0x35,0x36,0x37,0x38,0x39,0x3a,0x3b,0x3c,0x3d,0x3e,0x3f,
0x40,0xc1,0xc2,0xc3,0xc4,0xc5,0xc6,0xc7,0xc8,0xc9,0xca,0xcb,0xcc,0xcd,0xce,0xcf,
0xd0,0xd1,0xd2,0xd3,0xd4,0xd5,0xd6,0xd7,0xd8,0xd9,0xda,0x5b,0x5c,0x5d,0x5e,0x5f,
0xc0,0x41,0x42,0x43,0x44,0x45,0x46,0x47,0x48,0x49,0x4a,0x4b,0x4c,0x4d,0x4e,0x4f,
0x50,0x51,0x52,0x53,0x54,0x55,0x56,0x57,0x58,0x59,0x5a,0xdb,0xdc,0xdd,0xde,0xdf,
0x80,0x81,0x82,0x83,0x84,0x85,0x86,0x87,0x88,0x89,0x8a,0x8b,0x8c,0x8d,0x8e,0x8f,
0x90,0x91,0x92,0x0c,0x94,0x95,0x96,0x97,0x98,0x99,0x9a,0x9b,0x9c,0x9d,0x9e,0x9f,
0xa0,0xa1,0xa2,0xa3,0xa4,0xa5,0xa6,0xa7,0xa8,0xa9,0xaa,0xab,0xac,0xad,0xae,0xaf,
0xb0,0xb1,0xb2,0xb3,0xb4,0xb5,0xb6,0xb7,0xb8,0xb9,0xba,0xbb,0xbc,0xbd,0xbe,0xbf,
0x60,0x61,0x62,0x63,0x64,0x65,0x66,0x67,0x68,0x69,0x6a,0x6b,0x6c,0x6d,0x6e,0x6f,
0x70,0x71,0x72,0x73,0x74,0x75,0x76,0x77,0x78,0x79,0x7a,0x7b,0x7c,0x7d,0x7e,0x7f,
0xe0,0xe1,0xe2,0xe3,0xe4,0xe5,0xe6,0xe7,0xe8,0xe9,0xea,0xeb,0xec,0xed,0xee,0xef,
0xf0,0xf1,0xf2,0xf3,0xf4,0xf5,0xf6,0xf7,0xf8,0xf9,0xfa,0xfb,0xfc,0xfd,0xfe,0xff
};
#define VERSIONA 0
#define VERSIONB 1
#define VERSION_ADDRESS 0 // EEPROM address
#define VERSION_LEN 2 // Length in bytes
#define SSID_ADDRESS 2
#define SSID_LEN 32
#define PASS_ADDRESS 34
#define PASS_LEN 63
#define IP_TYPE_ADDRESS 97 // for future use
#define STATIC_IP_ADDRESS 98 // length 4, for future use
#define STATIC_GW 102 // length 4, for future use
#define STATIC_DNS 106 // length 4, for future use
#define STATIC_MASK 110 // length 4, for future use
#define BAUD_ADDRESS 111
#define ECHO_ADDRESS 112
#define SERVER_PORT_ADDRESS 113 // 2 bytes
#define AUTO_ANSWER_ADDRESS 115 // 1 byte
#define TELNET_ADDRESS 116 // 1 byte
#define VERBOSE_ADDRESS 117
#define PET_TRANSLATE_ADDRESS 118
#define FLOW_CONTROL_ADDRESS 119
#define PIN_POLARITY_ADDRESS 120
#define DIAL0_ADDRESS 200
#define DIAL1_ADDRESS 250
#define DIAL2_ADDRESS 300
#define DIAL3_ADDRESS 350
#define DIAL4_ADDRESS 400
#define DIAL5_ADDRESS 450
#define DIAL6_ADDRESS 500
#define DIAL7_ADDRESS 550
#define DIAL8_ADDRESS 600
#define DIAL9_ADDRESS 650
#define BUSY_MSG_ADDRESS 700
#define BUSY_MSG_LEN 80
#define LAST_ADDRESS 780
#define SWITCH_PIN 0 // GPIO0 (programmind mode pin)
#define LED_PIN 12 // Status LED
#define DCD_PIN 2 // DCD Carrier Status
#define RTS_PIN 4 // RTS Request to Send, connect to host's CTS pin
#define CTS_PIN 5 // CTS Clear to Send, connect to host's RTS pin
// Global variables
String build = "20160621182048";
String cmd = ""; // Gather a new AT command to this string from serial
bool cmdMode = true; // Are we in AT command mode or connected mode
bool callConnected = false;// Are we currently in a call
bool telnet = false; // Is telnet control code handling enabled
bool verboseResults = false;
//#define DEBUG 1 // Print additional debug information to serial channel
#undef DEBUG
#define LISTEN_PORT 6400 // Listen to this if not connected. Set to zero to disable.
int tcpServerPort = LISTEN_PORT;
#define RING_INTERVAL 3000 // How often to print RING when having a new incoming connection (ms)
unsigned long lastRingMs = 0; // Time of last "RING" message (millis())
//long myBps; // What is the current BPS setting
#define MAX_CMD_LENGTH 256 // Maximum length for AT command
char plusCount = 0; // Go to AT mode at "+++" sequence, that has to be counted
unsigned long plusTime = 0;// When did we last receive a "+++" sequence
#define LED_TIME 15 // How many ms to keep LED on at activity
unsigned long ledTime = 0;
#define TX_BUF_SIZE 256 // Buffer where to read from serial before writing to TCP
// (that direction is very blocking by the ESP TCP stack,
// so we can't do one byte a time.)
uint8_t txBuf[TX_BUF_SIZE];
const int speedDialAddresses[] = { DIAL0_ADDRESS, DIAL1_ADDRESS, DIAL2_ADDRESS, DIAL3_ADDRESS, DIAL4_ADDRESS, DIAL5_ADDRESS, DIAL6_ADDRESS, DIAL7_ADDRESS, DIAL8_ADDRESS, DIAL9_ADDRESS };
String speedDials[10];
const int bauds[] = { 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 };
byte serialspeed;
bool echo = true;
bool autoAnswer = false;
String ssid, password, busyMsg;
byte ringCount = 0;
String resultCodes[] = { "OK", "CONNECT", "RING", "NO CARRIER", "ERROR", "", "NO DIALTONE", "BUSY", "NO ANSWER" };
enum resultCodes_t { R_OK, R_CONNECT, R_RING, R_NOCARRIER, R_ERROR, R_NONE, R_NODIALTONE, R_BUSY, R_NOANSWER };
unsigned long connectTime = 0;
bool petTranslate = false; // Fix PET MCTerm 1.26C Pet->ASCII encoding to actual ASCII
bool hex = false;
enum flowControl_t { F_NONE, F_HARDWARE, F_SOFTWARE };
byte flowControl = F_NONE; // Use flow control
bool txPaused = false; // Has flow control asked us to pause?
enum pinPolarity_t { P_INVERTED, P_NORMAL }; // Is LOW (0) or HIGH (1) active?
byte pinPolarity = P_INVERTED;
// Telnet codes
#define DO 0xfd
#define WONT 0xfc
#define WILL 0xfb
#define DONT 0xfe
WiFiClient tcpClient;
WiFiServer tcpServer(tcpServerPort);
ESP8266WebServer webServer(80);
MDNSResponder mdns;
String connectTimeString() {
unsigned long now = millis();
int secs = (now - connectTime) / 1000;
int mins = secs / 60;
int hours = mins / 60;
String out = "";
if (hours < 10) out.concat("0");
out.concat(String(hours));
out.concat(":");
if (mins % 60 < 10) out.concat("0");
out.concat(String(mins % 60));
out.concat(":");
if (secs % 60 < 10) out.concat("0");
out.concat(String(secs % 60));
return out;
}
void writeSettings() {
setEEPROM(ssid, SSID_ADDRESS, SSID_LEN);
setEEPROM(password, PASS_ADDRESS, PASS_LEN);
setEEPROM(busyMsg, BUSY_MSG_ADDRESS, BUSY_MSG_LEN);
EEPROM.write(BAUD_ADDRESS, serialspeed);
EEPROM.write(ECHO_ADDRESS, byte(echo));
EEPROM.write(AUTO_ANSWER_ADDRESS, byte(autoAnswer));
EEPROM.write(SERVER_PORT_ADDRESS, highByte(tcpServerPort));
EEPROM.write(SERVER_PORT_ADDRESS + 1, lowByte(tcpServerPort));
EEPROM.write(TELNET_ADDRESS, byte(telnet));
EEPROM.write(VERBOSE_ADDRESS, byte(verboseResults));
EEPROM.write(PET_TRANSLATE_ADDRESS, byte(petTranslate));
EEPROM.write(FLOW_CONTROL_ADDRESS, byte(flowControl));
EEPROM.write(PIN_POLARITY_ADDRESS, byte(pinPolarity));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
setEEPROM(speedDials[i], speedDialAddresses[i], 50);
}
EEPROM.commit();
}
void readSettings() {
echo = EEPROM.read(ECHO_ADDRESS);
autoAnswer = EEPROM.read(AUTO_ANSWER_ADDRESS);
// serialspeed = EEPROM.read(BAUD_ADDRESS);
// This is where the WIFI name and pass are set for the session.
// If your SSID contains an underscore, you will either need to re-name
// your network, or hard-set its name here, because CBM charset has no
// underscore and you won't be able to type it in live on the C64 itself.
ssid = getEEPROM(SSID_ADDRESS, SSID_LEN);
password = getEEPROM(PASS_ADDRESS, PASS_LEN);
// ssid = "YOUR_SSID";
// password = "YOUR_PASS";
busyMsg = getEEPROM(BUSY_MSG_ADDRESS, BUSY_MSG_LEN);
tcpServerPort = word(EEPROM.read(SERVER_PORT_ADDRESS), EEPROM.read(SERVER_PORT_ADDRESS + 1));
telnet = EEPROM.read(TELNET_ADDRESS);
verboseResults = EEPROM.read(VERBOSE_ADDRESS);
petTranslate = EEPROM.read(PET_TRANSLATE_ADDRESS);
flowControl = EEPROM.read(FLOW_CONTROL_ADDRESS);
pinPolarity = EEPROM.read(PIN_POLARITY_ADDRESS);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
speedDials[i] = getEEPROM(speedDialAddresses[i], 50);
}
}
void defaultEEPROM() {
EEPROM.write(VERSION_ADDRESS, VERSIONA);
EEPROM.write(VERSION_ADDRESS + 1, VERSIONB);
setEEPROM("Weaselhaus_24", SSID_ADDRESS, SSID_LEN);
setEEPROM("Securicode.12", PASS_ADDRESS, PASS_LEN);
setEEPROM("d", IP_TYPE_ADDRESS, 1);
EEPROM.write(SERVER_PORT_ADDRESS, highByte(LISTEN_PORT));
EEPROM.write(SERVER_PORT_ADDRESS + 1, lowByte(LISTEN_PORT));
EEPROM.write(BAUD_ADDRESS, 0x00);
EEPROM.write(ECHO_ADDRESS, 0x01);
EEPROM.write(AUTO_ANSWER_ADDRESS, 0x01);
EEPROM.write(TELNET_ADDRESS, 0x00);
EEPROM.write(VERBOSE_ADDRESS, 0x01);
EEPROM.write(PET_TRANSLATE_ADDRESS, 0x00);
EEPROM.write(FLOW_CONTROL_ADDRESS, 0x00);
EEPROM.write(PIN_POLARITY_ADDRESS, 0x01);
setEEPROM("bbs.fozztexx.com:23", speedDialAddresses[0], 50);
setEEPROM("cottonwoodbbs.dyndns.org:6502", speedDialAddresses[1], 50);
setEEPROM("borderlinebbs.dyndns.org:6400", speedDialAddresses[2], 50);
setEEPROM("particlesbbs.dyndns.org:6400", speedDialAddresses[3], 50);
setEEPROM("reflections.servebbs.com:23", speedDialAddresses[4], 50);
setEEPROM("heatwavebbs.com:9640", speedDialAddresses[5], 50);
for (int i = 5; i < 10; i++) {
setEEPROM("", speedDialAddresses[i], 50);
}
setEEPROM("SYSTEM BUSY. TRY AGAIN LATER.", BUSY_MSG_ADDRESS, BUSY_MSG_LEN);
EEPROM.commit();
}
String getEEPROM(int startAddress, int len) {
String myString;
for (int i = startAddress; i < startAddress + len; i++) {
if (EEPROM.read(i) == 0x00) {
break;
}
myString += char(EEPROM.read(i));
//Serial.print(char(EEPROM.read(i)));
}
//Serial.println();
return myString;
}
void setEEPROM(String inString, int startAddress, int maxLen) {
for (int i = startAddress; i < inString.length() + startAddress; i++) {
EEPROM.write(i, inString[i - startAddress]);
//Serial.print(i, DEC); Serial.print(": "); Serial.println(inString[i - startAddress]);
//if (EEPROM.read(i) != inString[i - startAddress]) { Serial.print(" (!)"); }
//Serial.println();
}
// null pad the remainder of the memory space
for (int i = inString.length() + startAddress; i < maxLen + startAddress; i++) {
EEPROM.write(i, 0x00);
//Serial.print(i, DEC); Serial.println(": 0x00");
}
}
void sendResult(int resultCode) {
Serial.print("\r\n");
if (verboseResults == 0) {
Serial.println(resultCode);
return;
}
if (resultCode == R_CONNECT) {
Serial.print(String(resultCodes[R_CONNECT]) + " " + String(bauds[serialspeed]));
} else if (resultCode == R_NOCARRIER) {
Serial.print(String(resultCodes[R_NOCARRIER]) + " (" + connectTimeString() + ")");
} else {
Serial.print(String(resultCodes[resultCode]));
}
Serial.print("\r\n");
}
void sendString(String msg) {
Serial.print("\r\n");
Serial.print(msg);
Serial.print("\r\n");
}
// Hold for 5 seconds to switch to 300 baud
// Slow flash: keep holding
// Fast flash: let go
int checkButton() {
long time = millis();
while (digitalRead(SWITCH_PIN) == LOW && millis() - time < 5000) {
delay(250);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, !digitalRead(LED_PIN));
yield();
}
if (millis() - time > 5000) {
Serial.flush();
Serial.end();
serialspeed = 0;
delay(100);
Serial.begin(bauds[serialspeed]);
sendResult(R_OK);
while (digitalRead(SWITCH_PIN) == LOW) {
delay(50);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, !digitalRead(LED_PIN));
yield();
}
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
void connectWiFi() {
if (ssid == "" || password == "") {
Serial.println("NEED TO CONFIGURE SSID AND PASSWORD. TYPE AT? FOR HELP.");
return;
}
// ### ADDED DW-11/24/2023
// This section ensures the ESP connects most quickly to the access point
WiFi.persistent(true);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
// ###
WiFi.begin(ssid.c_str(), password.c_str());
// WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("\nCONNECTING TO "); Serial.print(ssid);
uint8_t i = 0;
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED && i++ < 60) {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
delay(250);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
delay(250);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println();
if (i == 61) { //one more tick than the value set in Wifi.status above
Serial.print("COULD NOT CONNECT TO "); Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.disconnect();
updateLed();
} else {
Serial.print("CONNECTED TO "); Serial.println(WiFi.SSID());
Serial.print("IP ADDRESS: "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
updateLed();
}
}
void updateLed() {
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); // on
} else {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); //off
}
}
void disconnectWiFi() {
WiFi.disconnect();
updateLed();
}
void setBaudRate(int inSpeed) {
if (inSpeed == 0) {
sendResult(R_ERROR);
return;
}
int foundBaud = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(bauds); i++) {
if (inSpeed == bauds[i]) {
foundBaud = i;
break;
}
}
// requested baud rate not found, return error
if (foundBaud == -1) {
sendResult(R_ERROR);
return;
}
if (foundBaud == serialspeed) {
sendResult(R_OK);
return;
}
Serial.print("SWITCHING SERIAL PORT TO ");
Serial.print(inSpeed);
Serial.println(" IN 5 SECONDS");
delay(5000);
Serial.end();
delay(200);
Serial.begin(bauds[foundBaud]);
serialspeed = foundBaud;
delay(200);
sendResult(R_OK);
}
void setCarrier(byte carrier) {
if (pinPolarity == P_NORMAL) carrier = !carrier;
digitalWrite(DCD_PIN, carrier);
}
void displayNetworkStatus() {
Serial.print("WIFI STATUS: ");
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.println("CONNECTED");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_IDLE_STATUS) {
Serial.println("OFFLINE");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECT_FAILED) {
Serial.println("CONNECT FAILED");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_NO_SSID_AVAIL) {
Serial.println("SSID UNAVAILABLE");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTION_LOST) {
Serial.println("CONNECTION LOST");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_DISCONNECTED) {
Serial.println("DISCONNECTED");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_SCAN_COMPLETED) {
Serial.println("SCAN COMPLETED");
}
yield();
Serial.print("SSID.......: "); Serial.println(WiFi.SSID());
// Serial.print("ENCRYPTION: ");
// switch(WiFi.encryptionType()) {
// case 2:
// Serial.println("TKIP (WPA)");
// break;
// case 5:
// Serial.println("WEP");
// break;
// case 4:
// Serial.println("CCMP (WPA)");
// break;
// case 7:
// Serial.println("NONE");
// break;
// case 8:
// Serial.println("AUTO");
// break;
// default:
// Serial.println("UNKNOWN");
// break;
// }
byte mac[6];
WiFi.macAddress(mac);
Serial.print("MAC ADDRESS: ");
Serial.print(mac[0], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[1], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[2], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[3], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[4], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(mac[5], HEX);
yield();
Serial.print("IP ADDRESS.: "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); yield();
Serial.print("GATEWAY....: "); Serial.println(WiFi.gatewayIP()); yield();
Serial.print("SUBNET MASK: "); Serial.println(WiFi.subnetMask()); yield();
Serial.print("SERVER PORT: "); Serial.println(tcpServerPort); yield();
Serial.print("WEB CONFIG.: HTTP://"); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); yield();
Serial.print("CALL STATUS: "); yield();
if (callConnected) {
Serial.print("CONNECTED TO "); Serial.println(ipToString(tcpClient.remoteIP())); yield();
Serial.print("CALL LENGTH: "); Serial.println(connectTimeString()); yield();
} else {
Serial.println("NOT CONNECTED");
}
}
void displayCurrentSettings() {
Serial.println("ACTIVE PROFILE:"); yield();
Serial.print("BAUD: "); Serial.println(bauds[serialspeed]); yield();
Serial.print("SSID: "); Serial.println(ssid); yield();
Serial.print("PASS: "); Serial.println(password); yield();
//Serial.print("SERVER TCP PORT: "); Serial.println(tcpServerPort); yield();
Serial.print("BUSY MSG: "); Serial.println(busyMsg); yield();
Serial.print("E"); Serial.print(echo); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("V"); Serial.print(verboseResults); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("&K"); Serial.print(flowControl); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("&P"); Serial.print(pinPolarity); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("NET"); Serial.print(telnet); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("PET"); Serial.print(petTranslate); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("S0:"); Serial.print(autoAnswer); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.println(); yield();
Serial.println("SPEED DIAL:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Serial.print(i); Serial.print(": "); Serial.println(speedDials[i]);
yield();
}
Serial.println();
}
void displayStoredSettings() {
Serial.println("STORED PROFILE:"); yield();
Serial.print("BAUD: "); Serial.println(bauds[EEPROM.read(BAUD_ADDRESS)]); yield();
Serial.print("SSID: "); Serial.println(getEEPROM(SSID_ADDRESS, SSID_LEN)); yield();
Serial.print("PASS: "); Serial.println(getEEPROM(PASS_ADDRESS, PASS_LEN)); yield();
//Serial.print("SERVER TCP PORT: "); Serial.println(word(EEPROM.read(SERVER_PORT_ADDRESS), EEPROM.read(SERVER_PORT_ADDRESS+1))); yield();
Serial.print("BUSY MSG: "); Serial.println(getEEPROM(BUSY_MSG_ADDRESS, BUSY_MSG_LEN)); yield();
Serial.print("E"); Serial.print(EEPROM.read(ECHO_ADDRESS)); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("V"); Serial.print(EEPROM.read(VERBOSE_ADDRESS)); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("&K"); Serial.print(EEPROM.read(FLOW_CONTROL_ADDRESS)); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("&P"); Serial.print(EEPROM.read(PIN_POLARITY_ADDRESS)); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("NET"); Serial.print(EEPROM.read(TELNET_ADDRESS)); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("PET"); Serial.print(EEPROM.read(PET_TRANSLATE_ADDRESS)); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.print("S0:"); Serial.print(EEPROM.read(AUTO_ANSWER_ADDRESS)); Serial.print(" "); yield();
Serial.println(); yield();
Serial.println("STORED SPEED DIAL:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Serial.print(i); Serial.print(": "); Serial.println(getEEPROM(speedDialAddresses[i], 50));
yield();
}
Serial.println();
}
void waitForSpace() {
Serial.print("PRESS SPACE");
char c = 0;
while (c != 0x20) {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
c = Serial.read();
if (petTranslate == true){
if (c > 127) c-= 128;
}
}
}
Serial.print("\r");
}
void displayHelp() {
welcome();
Serial.println("AT COMMAND SUMMARY:"); yield();
Serial.println("DIAL HOST.....: ATDTHOST:PORT"); yield();
Serial.println("SPEED DIAL....: ATDSN (N=0-9)"); yield();
Serial.println("SET SPEED DIAL: AT&ZN=HOST:PORT (N=0-9)"); yield();
Serial.println("HANDLE TELNET.: ATNETN (N=0,1)"); yield();
Serial.println("PET MCTERM TR.: ATPETN (N=0,1)"); yield();
Serial.println("NETWORK INFO..: ATI"); yield();
Serial.println("HTTP GET......: ATGET<URL>"); yield();
//Serial.println("SERVER PORT...: AT$SP=N (N=1-65535)"); yield();
Serial.println("AUTO ANSWER...: ATS0=N (N=0,1)"); yield();
Serial.println("SET BUSY MSG..: AT$BM=YOUR BUSY MESSAGE"); yield();
Serial.println("LOAD NVRAM....: ATZ"); yield();
Serial.println("SAVE TO NVRAM.: AT&W"); yield();
Serial.println("SHOW SETTINGS.: AT&V"); yield();
Serial.println("FACT. DEFAULTS: AT&F"); yield();
Serial.println("PIN POLARITY..: AT&PN (N=0/INV,1/NORM)"); yield();
Serial.println("ECHO OFF/ON...: ATE0 / ATE1"); yield();
Serial.println("VERBOSE OFF/ON: ATV0 / ATV1"); yield();
Serial.println("SET SSID......: AT$SSID=WIFISSID"); yield();
Serial.println("SET PASSWORD..: AT$PASS=WIFIPASSWORD"); yield();
Serial.println("SET BAUD RATE.: AT$SB=N (3,12,24,48,96"); yield();
Serial.println(" 192,384,576,1152)*100"); yield();
waitForSpace();
Serial.println("FLOW CONTROL..: AT&KN (N=0/N,1/HW,2/SW)"); yield();
Serial.println("WIFI OFF/ON...: ATC0 / ATC1"); yield();
Serial.println("HANGUP........: ATH"); yield();
Serial.println("ENTER CMD MODE: +++"); yield();
Serial.println("EXIT CMD MODE.: ATO"); yield();
Serial.println("QUERY MOST COMMANDS FOLLOWED BY '?'"); yield();
}
void storeSpeedDial(byte num, String location) {
//if (num < 0 || num > 9) { return; }
speedDials[num] = location;
//Serial.print("STORED "); Serial.print(num); Serial.print(": "); Serial.println(location);
}
void welcome() {
Serial.println();
Serial.println("STRIKELINK! BY ALWYZ, MOD BY DEADWEASEL");
Serial.println("BASED ON GITHUB.COM/JSALIN/ESP8266_MODEM");
}
/**
Arduino main init function
*/
void setup() {
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); // off
pinMode(SWITCH_PIN, INPUT);
digitalWrite(SWITCH_PIN, HIGH);
pinMode(DCD_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RTS_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RTS_PIN, HIGH); // ready to receive data
pinMode(CTS_PIN, INPUT);
//digitalWrite(CTS_PIN, HIGH); // pull up
setCarrier(false);
EEPROM.begin(LAST_ADDRESS + 1);
delay(10);
if (EEPROM.read(VERSION_ADDRESS) != VERSIONA || EEPROM.read(VERSION_ADDRESS + 1) != VERSIONB) {
defaultEEPROM();
}
readSettings();
// Fetch baud rate from EEPROM
serialspeed = EEPROM.read(BAUD_ADDRESS);
// Check if it's out of bounds-- we have to be able to talk
if (serialspeed < 0 || serialspeed > sizeof(bauds)) {
serialspeed = 0;
}
Serial.begin(bauds[serialspeed]);
char c;
//unsigned long startMillis = millis();
//while (c != 8 && c != 127 && c!= 20) { // Check for the backspace key to begin
//while (c != 32) { // Check for space to begin
while (c != 0x0a && c != 0x0d) {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
c = Serial.read();
if (petTranslate == true){
if (c > 127) c-= 128;
}
}
if (checkButton() == 1) {
break; // button pressed, we're setting to 300 baud and moving on
}
//if (millis() - startMillis > 2000) {
//digitalWrite(LED_PIN, !digitalRead(LED_PIN));
//startMillis = millis();
//}
yield();
}
welcome();
if (tcpServerPort > 0) tcpServer.begin();
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
connectWiFi();
sendResult(R_OK);
//tcpServer(tcpServerPort); // can't start tcpServer inside a function-- must live outside
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); // on
webServer.on("/", handleRoot);
webServer.on("/ath", handleWebHangUp);
webServer.begin();
mdns.begin("C64WiFi", WiFi.localIP());
}
String ipToString(IPAddress ip) {
char s[16];
sprintf(s, "%d.%d.%d.%d", ip[0], ip[1], ip[2], ip[3]);
return s;
}
void hangUp() {
tcpClient.stop();
callConnected = false;
setCarrier(callConnected);
sendResult(R_NOCARRIER);
connectTime = 0;
}
void handleWebHangUp() {
String t = "NO CARRIER (" + connectTimeString() + ")";
hangUp();
webServer.send(200, "text/plain", t);
}
void handleRoot() {
String page = "WIFI STATUS: ";
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) {
page.concat("CONNECTED");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_IDLE_STATUS) {
page.concat("OFFLINE");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECT_FAILED) {
page.concat("CONNECT FAILED");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_NO_SSID_AVAIL) {
page.concat("SSID UNAVAILABLE");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTION_LOST) {
page.concat("CONNECTION LOST");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_DISCONNECTED) {
page.concat("DISCONNECTED");
}
if (WiFi.status() == WL_SCAN_COMPLETED) {
page.concat("SCAN COMPLETED");
}
yield();
page.concat("\nSSID.......: " + WiFi.SSID());
byte mac[6];
WiFi.macAddress(mac);
page.concat("\nMAC ADDRESS: ");
page.concat(String(mac[0], HEX));
page.concat(":");
page.concat(String(mac[1], HEX));
page.concat(":");
page.concat(String(mac[2], HEX));
page.concat(":");
page.concat(String(mac[3], HEX));
page.concat(":");
page.concat(String(mac[4], HEX));
page.concat(":");
page.concat(String(mac[5], HEX));
yield();
page.concat("\nIP ADDRESS.: "); page.concat(ipToString(WiFi.localIP()));
page.concat("\nGATEWAY....: "); page.concat(ipToString(WiFi.gatewayIP()));
yield();
page.concat("\nSUBNET MASK: "); page.concat(ipToString(WiFi.subnetMask()));
yield();
page.concat("\nSERVER PORT: "); page.concat(tcpServerPort);
page.concat("\nCALL STATUS: ");
if (callConnected) {
page.concat("CONNECTED TO ");
page.concat(ipToString(tcpClient.remoteIP()));
page.concat("\nCALL LENGTH: "); page.concat(connectTimeString()); yield();
} else {
page.concat("NOT CONNECTED");
}
page.concat("\n");
webServer.send(200, "text/plain", page);
delay(100);
}
/**
Turn on the LED and store the time, so the LED will be shortly after turned off
*/
void led_on()
{
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, !digitalRead(LED_PIN));
ledTime = millis();
}
void answerCall() {
tcpClient = tcpServer.available();
tcpClient.setNoDelay(true); // try to disable naggle
//tcpServer.stop();
sendResult(R_CONNECT);
connectTime = millis();
cmdMode = false;
callConnected = true;
setCarrier(callConnected);
Serial.flush();
}
void handleIncomingConnection() {
if (callConnected == 1 || (autoAnswer == false && ringCount > 3)) {
// We're in a call already or didn't answer the call after three rings
// We didn't answer the call. Notify our party we're busy and disconnect
ringCount = lastRingMs = 0;
WiFiClient anotherClient = tcpServer.available();
anotherClient.print(busyMsg);
anotherClient.print("\r\n");
anotherClient.print("CURRENT CALL LENGTH: ");
anotherClient.print(connectTimeString());
anotherClient.print("\r\n");
anotherClient.print("\r\n");
anotherClient.flush();
anotherClient.stop();
return;
}
if (autoAnswer == false) {
if (millis() - lastRingMs > 6000 || lastRingMs == 0) {
lastRingMs = millis();
sendResult(R_RING);
ringCount++;
}
return;
}
if (autoAnswer == true) {
WiFiClient tempClient = tcpServer.available(); // this is the key to keeping the connection open
tcpClient = tempClient; // hand over the new connection to the global client
tempClient.stop(); // stop the temporary one
sendString(String("RING ") + ipToString(tcpClient.remoteIP()));
delay(1000);
sendResult(R_CONNECT);
connectTime = millis();
cmdMode = false;
tcpClient.flush();
callConnected = true;
setCarrier(callConnected);
}
}
void dialOut(String upCmd) {
// Can't place a call while in a call
if (callConnected) {
sendResult(R_ERROR);
return;
}
String host, port;
int portIndex;
// Dialing a stored number
if (upCmd.indexOf("ATDS") == 0) {
byte speedNum = upCmd.substring(4, 5).toInt();
portIndex = speedDials[speedNum].indexOf(':');
if (portIndex != -1) {
host = speedDials[speedNum].substring(0, portIndex);
port = speedDials[speedNum].substring(portIndex + 1);
} else {
port = "23";
}
} else {
// Dialing an ad-hoc number
int portIndex = cmd.indexOf(":");
if (portIndex != -1)
{
host = cmd.substring(4, portIndex);
port = cmd.substring(portIndex + 1, cmd.length());
}
else
{
host = cmd.substring(4, cmd.length());
port = "23"; // Telnet default
}
}
host.trim(); // remove leading or trailing spaces
port.trim();
Serial.print("DIALING "); Serial.print(host); Serial.print(":"); Serial.println(port);
char *hostChr = new char[host.length() + 1];
host.toCharArray(hostChr, host.length() + 1);
int portInt = port.toInt();
tcpClient.setNoDelay(true); // Try to disable naggle
if (tcpClient.connect(hostChr, portInt))
{
tcpClient.setNoDelay(true); // Try to disable naggle
sendResult(R_CONNECT);
connectTime = millis();
cmdMode = false;
Serial.flush();
callConnected = true;
setCarrier(callConnected);
//if (tcpServerPort > 0) tcpServer.stop();
}
else
{
sendResult(R_NOANSWER);
callConnected = false;
setCarrier(callConnected);
}
delete hostChr;
}
/**
Perform a command given in command mode
*/
void command()
{
cmd.trim();
if (cmd == "") return;
Serial.println();
String upCmd = cmd;
upCmd.toUpperCase();
/**** Just AT ****/
if (upCmd == "AT") sendResult(R_OK);
/**** Dial to host ****/
else if ((upCmd.indexOf("ATDT") == 0) || (upCmd.indexOf("ATDP") == 0) || (upCmd.indexOf("ATDI") == 0) || (upCmd.indexOf("ATDS") == 0))
{
dialOut(upCmd);
}
/**** Change telnet mode ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATNET0")
{
telnet = false;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else if (upCmd == "ATNET1")
{
telnet = true;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else if (upCmd == "ATNET?") {
Serial.println(String(telnet));
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Answer to incoming connection ****/
else if ((upCmd == "ATA") && tcpServer.hasClient()) {
answerCall();
}
/**** Display Help ****/
else if (upCmd == "AT?" || upCmd == "ATHELP") {
displayHelp();
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Reset, reload settings from EEPROM ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATZ") {
readSettings();
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Disconnect WiFi ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATC0") {
disconnectWiFi();
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Connect WiFi ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATC1") {
connectWiFi();
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Control local echo in command mode ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("ATE") == 0) {
if (upCmd.substring(3, 4) == "?") {
sendString(String(echo));
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else if (upCmd.substring(3, 4) == "0") {
echo = 0;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else if (upCmd.substring(3, 4) == "1") {
echo = 1;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else {
sendResult(R_ERROR);
}
}
/**** Control verbosity ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("ATV") == 0) {
if (upCmd.substring(3, 4) == "?") {
sendString(String(verboseResults));
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else if (upCmd.substring(3, 4) == "0") {
verboseResults = 0;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else if (upCmd.substring(3, 4) == "1") {
verboseResults = 1;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else {
sendResult(R_ERROR);
}
}
/**** Control pin polarity of CTS, RTS, DCD ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT&P") == 0) {
if (upCmd.substring(4, 5) == "?") {
sendString(String(pinPolarity));
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else if (upCmd.substring(4, 5) == "0") {
pinPolarity = P_INVERTED;
sendResult(R_OK);
setCarrier(callConnected);
}
else if (upCmd.substring(4, 5) == "1") {
pinPolarity = P_NORMAL;
sendResult(R_OK);
setCarrier(callConnected);
}
else {
sendResult(R_ERROR);
}
}
/**** Control Flow Control ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT&K") == 0) {
if (upCmd.substring(4, 5) == "?") {
sendString(String(flowControl));
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else if (upCmd.substring(4, 5) == "0") {
flowControl = 0;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else if (upCmd.substring(4, 5) == "1") {
flowControl = 1;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else if (upCmd.substring(4, 5) == "2") {
flowControl = 2;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
else {
sendResult(R_ERROR);
}
}
/**** Set current baud rate ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT$SB=") == 0) {
setBaudRate(upCmd.substring(6).toInt());
}
/**** Display current baud rate ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT$SB?") == 0) {
sendString(String(bauds[serialspeed]));;
}
/**** Set busy message ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT$BM=") == 0) {
busyMsg = cmd.substring(6);
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Display busy message ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT$BM?") == 0) {
sendString(busyMsg);
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Display Network settings ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATI") {
displayNetworkStatus();
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Display profile settings ****/
else if (upCmd == "AT&V") {
displayCurrentSettings();
waitForSpace();
displayStoredSettings();
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Save (write) current settings to EEPROM ****/
else if (upCmd == "AT&W") {
writeSettings();
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Set or display a speed dial number ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT&Z") == 0) {
byte speedNum = upCmd.substring(4, 5).toInt();
if (speedNum >= 0 && speedNum <= 9) {
if (upCmd.substring(5, 6) == "=") {
String speedDial = cmd;
storeSpeedDial(speedNum, speedDial.substring(6));
sendResult(R_OK);
}
if (upCmd.substring(5, 6) == "?") {
sendString(speedDials[speedNum]);
sendResult(R_OK);
}
} else {
sendResult(R_ERROR);
}
}
/**** Set WiFi SSID ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT$SSID=") == 0) {
ssid = cmd.substring(8);
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Display WiFi SSID ****/
else if (upCmd == "AT$SSID?") {
sendString(ssid);
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Set WiFi Password ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT$PASS=") == 0) {
password = cmd.substring(8);
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Display WiFi Password ****/
else if (upCmd == "AT$PASS?") {
sendString(password);
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Reset EEPROM and current settings to factory defaults ****/
else if (upCmd == "AT&F") {
defaultEEPROM();
readSettings();
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Set auto answer off ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATS0=0") {
autoAnswer = false;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Set auto answer on ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATS0=1") {
autoAnswer = true;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Display auto answer setting ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATS0?") {
sendString(String(autoAnswer));
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Set PET MCTerm Translate On ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATPET=1") {
petTranslate = true;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Set PET MCTerm Translate Off ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATPET=0") {
petTranslate = false;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Display PET MCTerm Translate Setting ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATPET?") {
sendString(String(petTranslate));
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Set HEX Translate On ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATHEX=1") {
hex = true;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Set HEX Translate Off ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATHEX=0") {
hex = false;
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Hang up a call ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("ATH") == 0) {
hangUp();
}
/**** Hang up a call ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT$RB") == 0) {
sendResult(R_OK);
Serial.flush();
delay(500);
ESP.reset();
}
/**** Exit modem command mode, go online ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATO") {
if (callConnected == 1) {
sendResult(R_CONNECT);
cmdMode = false;
} else {
sendResult(R_ERROR);
}
}
/**** Set incoming TCP server port ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("AT$SP=") == 0) {
tcpServerPort = upCmd.substring(6).toInt();
sendString("CHANGES REQUIRES NV SAVE (AT&W) AND RESTART");
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** Display icoming TCP server port ****/
else if (upCmd == "AT$SP?") {
sendString(String(tcpServerPort));
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** See my IP address ****/
else if (upCmd == "ATIP?")
{
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
sendResult(R_OK);
}
/**** HTTP GET request ****/
else if (upCmd.indexOf("ATGET") == 0)
{
// From the URL, aquire required variables
// (12 = "ATGEThttp://")
int portIndex = cmd.indexOf(":", 12); // Index where port number might begin
int pathIndex = cmd.indexOf("/", 12); // Index first host name and possible port ends and path begins
int port;
String path, host;
if (pathIndex < 0)
{
pathIndex = cmd.length();
}
if (portIndex < 0)
{
port = 80;
portIndex = pathIndex;
}
else
{
port = cmd.substring(portIndex + 1, pathIndex).toInt();
}
host = cmd.substring(12, portIndex);
path = cmd.substring(pathIndex, cmd.length());
if (path == "") path = "/";
char *hostChr = new char[host.length() + 1];
host.toCharArray(hostChr, host.length() + 1);
// Establish connection
if (!tcpClient.connect(hostChr, port))
{
sendResult(R_NOCARRIER);
connectTime = 0;
callConnected = false;
setCarrier(callConnected);
}
else
{
sendResult(R_CONNECT);
connectTime = millis();
cmdMode = false;
callConnected = true;
setCarrier(callConnected);
// Send a HTTP request before continuing the connection as usual
String request = "GET ";
request += path;
request += " HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: ";
request += host;
request += "\r\nConnection: close\r\n\r\n";
tcpClient.print(request);
}
delete hostChr;
}
/**** Unknown command ****/
else sendResult(R_ERROR);
cmd = "";
}
// RTS/CTS protocol is a method of handshaking which uses one wire in each direction to allow each
// device to indicate to the other whether or not it is ready to receive data at any given moment.
// One device sends on RTS and listens on CTS; the other does the reverse. A device should drive
// its handshake-output wire low when it is ready to receive data, and high when it is not. A device
// that wishes to send data should not start sending any bytes while the handshake-input wire is low;
// if it sees the handshake wire go high, it should finish transmitting the current byte and then wait
// for the handshake wire to go low before transmitting any more.
// http://electronics.stackexchange.com/questions/38022/what-is-rts-and-cts-flow-control
void handleFlowControl() {
if (flowControl == F_NONE) return;
if (flowControl == F_HARDWARE) {
if (digitalRead(CTS_PIN) == pinPolarity) txPaused = true;
else txPaused = false;
}
if (flowControl == F_SOFTWARE) {
}
}
/**
Arduino main loop function
*/
void loop()
{
// Check flow control
handleFlowControl();
// Service the Web server
webServer.handleClient();
// Check to see if user is requesting rate change to 300 baud
checkButton();
// New unanswered incoming connection on server listen socket
if (tcpServer.hasClient()) {
handleIncomingConnection();
}
/**** AT command mode ****/
if (cmdMode == true)
{
// In command mode - don't exchange with TCP but gather characters to a string
if (Serial.available())
{
char chr = Serial.read();
if (petTranslate == true)
// Fix PET MCTerm 1.26C Pet->ASCII encoding to actual ASCII
if (chr > 127) chr-= 128;
else
// Convert uppercase PETSCII to lowercase ASCII (C64) in command mode only
if ((chr >= 193) && (chr <= 218)) chr-= 96;
// Return, enter, new line, carriage return.. anything goes to end the command
if ((chr == '\n') || (chr == '\r'))
{
command();
}
// Backspace or delete deletes previous character
else if ((chr == 8) || (chr == 127) || (chr == 20))
{
cmd.remove(cmd.length() - 1);
if (echo == true) {
Serial.write(chr);
}
}
else
{
if (cmd.length() < MAX_CMD_LENGTH) cmd.concat(chr);
if (echo == true) {
Serial.write(chr);
}
if (hex) {
Serial.print(chr, HEX);
}
}
}
}
/**** Connected mode ****/
else
{
// Transmit from terminal to TCP
if (Serial.available())
{
led_on();
// In telnet in worst case we have to escape every byte
// so leave half of the buffer always free
int max_buf_size;
if (telnet == true)
max_buf_size = TX_BUF_SIZE / 2;
else
max_buf_size = TX_BUF_SIZE;
// Read from serial, the amount available up to
// maximum size of the buffer
size_t len = std::min(Serial.available(), max_buf_size);
Serial.readBytes(&txBuf[0], len);
// Enter command mode with "+++" sequence
for (int i = 0; i < (int)len; i++)
{
if (txBuf[i] == '+') plusCount++; else plusCount = 0;
if (plusCount >= 3)
{
plusTime = millis();
}
if (txBuf[i] != '+')
{
plusCount = 0;
}
}
// Double (escape) every 0xff for telnet, shifting the following bytes
// towards the end of the buffer from that point
if (telnet == true)
{
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (txBuf[i] == 0xff)
{
for (int j = TX_BUF_SIZE - 1; j > i; j--)
{
txBuf[j] = txBuf[j - 1];
}
len++;
}
}
}
// Fix PET MCTerm 1.26C Pet->ASCII encoding to actual ASCII
if (petTranslate == true) {
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (txBuf[i] > 127) txBuf[i]-= 128;
}
}
// Write the buffer to TCP finally
tcpClient.write(&txBuf[0], len);
yield();
}
// Transmit from TCP to terminal
while (tcpClient.available() && txPaused == false)
{
led_on();
uint8_t rxByte = tcpClient.read();
// Is a telnet control code starting?
if ((telnet == true) && (rxByte == 0xff))
{
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.print("<t>");
#endif
rxByte = tcpClient.read();
if (rxByte == 0xff)
{
// 2 times 0xff is just an escaped real 0xff
Serial.write(0xff); Serial.flush();
}
else
{
// rxByte has now the first byte of the actual non-escaped control code
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.print(rxByte);
Serial.print(",");
#endif
uint8_t cmdByte1 = rxByte;
rxByte = tcpClient.read();
uint8_t cmdByte2 = rxByte;
// rxByte has now the second byte of the actual non-escaped control code
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.print(rxByte); Serial.flush();
#endif
// We are asked to do some option, respond we won't
if (cmdByte1 == DO)
{
tcpClient.write((uint8_t)255); tcpClient.write((uint8_t)WONT); tcpClient.write(cmdByte2);
}
// Server wants to do any option, allow it
else if (cmdByte1 == WILL)
{
tcpClient.write((uint8_t)255); tcpClient.write((uint8_t)DO); tcpClient.write(cmdByte2);
}
}
#ifdef DEBUG
Serial.print("</t>");
#endif
}
else
{
// Non-control codes pass through freely
Serial.write(rxByte); yield(); Serial.flush(); yield();
}
handleFlowControl();
}
}
// If we have received "+++" as last bytes from serial port and there
// has been over a second without any more bytes
if (plusCount >= 3)
{
if (millis() - plusTime > 1000)
{
//tcpClient.stop();
cmdMode = true;
sendResult(R_OK);
plusCount = 0;
}
}
// Go to command mode if TCP disconnected and not in command mode
if ((!tcpClient.connected()) && (cmdMode == false) && callConnected == true)
{
cmdMode = true;
sendResult(R_NOCARRIER);
connectTime = 0;
callConnected = false;
setCarrier(callConnected);
//if (tcpServerPort > 0) tcpServer.begin();
}
// Turn off tx/rx led if it has been lit long enough to be visible
if (millis() - ledTime > LED_TIME) digitalWrite(LED_PIN, !digitalRead(LED_PIN)); // toggle LED state
}
[/code]
Strikelink WiFi Instructions
I hope you enjoy your new Strikelink WiFi! The esp8266 module on the board has already been
flashed with the latest firmware and pre-configured for 9600 baud use.
To get the proper use out of your unit, do the following to set up:
- With your C64 powered OFF, Plug the Strikelink WiFi into the C64 User Port, Strikelink WiFi
Logo side UP. - Turn on computer, and load CCGMS 2017 v4
- Press F7 to enter the program settings menu, select UP9600 / EZ232 under modem type, and
change the baud rate to 9600 baud - Save Phonebook and Config
- Press Return to enter Terminal Mode
- Press Return. Your Strikelink should say hello to you!
- Press F8 to enter Anscii Mode (Anscii is a combination of Ascii and Ansi. CCGMS will interpret
Ansi colors in Ascii mode). Anscii mode helps the modem properly interpret your WiFi router
SSID and Password. - Type AT$SSID=YOURWIFINAMEGOESHERE (Then press Return)
- Type AT$PASS=YOURPASSWORDGOESHERE (Then press Return)
- Type ATC1 to Connect (ATC1 connects to your WiFi, ATC0 disconnects)
- Type AT&W to write your settings to the Strikelink WiFi. These will be permanently saved, so in the future, you can load CCGMS 2017 v4, press return, and you should automatically be ready to call BBSes. If your Strikelink ever fails to connect to your router / WiFi access point, just type
atc1 to try connecting again. - Press F8 to return to Graphics mode, and use the Autodialer in CCGMS 2017 v4 to start calling C64 BBS Systems. You can save your User ID and Password for BBSes in CCGMS 2017 v4 and send them to the BBS you call by pressing F6 and F8, respectively. It makes logging in much easier!
Notes:
- You should be able to stay in 9600 baud mode for most boards you call, even boards that run at lower baud rates. If you ever need to change your baud rate on the Strikelink, just type AT$SB=NEWBAUDRATE in terminal mode (ex. AT$SB=2400), then switch to the F7 menu in CCGMS 2017 v4 and select the corresponding baud rate (ex.2400). Return to terminal mode, and you will now be operating at your new baud rate.
- If you switch to use the User Port 300-2400 modem type in CCGMS 2017 v4 (instead of the UP9600 / EZ232 modem), you’ll need to turn off hardware flow control. AT&K0 will turn off hardware flow control. AT&K1 will turn it back on. You must have hardware flow control on when using the UP9600 / EZ232 modem or bad things will happen :). As the UP9600 / EZ232 modem setting should be fine for calling all BBS Systems, you should really never need to do this.
- The terminal command ‘AT?‘ should give you a list of available modem at commands. If this flies by too fast, switch to 2400 baud to see the full menu.
- If your WiFi ever stops working, use the reset button on the WiFi unit or power off your C64 and
restart your computer. - DO NOT USE external 5v usb power at the same time you have your Strikelink WiFi plugged in. This could damage your Strikelink or C64. If you wish to use external usb power instead of the C64 power, cut the trace going to pin 2 on the c64 user port. (top of the board, right side). The Strikelink could draw too much current on C64s not utilizing a newer heavy duty power supply, causing issues. In that case, cutting the trace and using external power is recommended.
How to use external USB power instead of C64 Power.
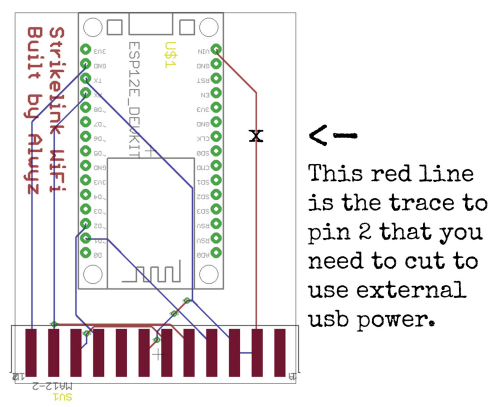
This is the top side of the board, with the Strikelink WiFi logo on the
left side.
You can use a small screwdriver edge or other small tool to cut the line on the board. To test if your cut was effective, plug your Strikelink WiFi into the C64 without the usb power plugged in, and make sure the blue light on the Strikelink WiFi does NOT turn on.
At this point it is safe to plug in external usb power.
When using external usb power, it is recommended to power on the Strikelink WiFi before turning on your C64.
In case of accidental firmware factory reset (at&f), set CCGMS to 300 baud to connect, then issue the following commands:
AT&P0
AT&K1
AT$SB=9600
Questions: http://1200baud.wordpress.com – alwyz@sceneworld.org



I’m trying to download the modem software but the download link gives a 404 and your site is not allowing me to highlight and copy the code that is under software. Thanks for any information.
Ahhh that would be because I am a dumbass and accidentally deleted the separate post that link used to point to, and I was also toying around with a site plugin to see what it did to site scraping bots. 😀
Anyway, I have fixed the link by uploading the zipped up version of the file, and turned off that blocking plugin.
Sorry about that!